Ground Storage
Ground Storage - the Simplest Type of Storage
Ground storage is a particularly uncomplicated type of storage in which load units are placed directly on the floor. This method makes ground storage one of the most cost-effective types of storage, as no shelving or storage racks are required, keeping investment costs low. Ground storage is particularly suitable for stackable goods such as drinks crates or barrels, building materials, bulk goods and seasonal goods that only need to be stored for a short period of time. There are various principles for efficient ground storage in warehouses or production facilities, which differ depending on the item structure and space requirements.
Ground Storage - Solves the following Problems!
Select one of the problems. You will receive instructions that you can use to calculate optimization potential.Low Available Storage Space
Storage and Retrieval errors
Large Quantities of Single-Grade Pallets
Picking Errors
Ground Storage - Find the Right Offering for You
Select products and receive detailed information. You can use the platform to contact product suppliersGround Storage - The Solution can be Combined with the Following Solutions
Here you can find solutions, which can be combined with the presented solution.Ground Storage - The Following Solutions can also Solve the Pain Point
Here you can find other solutions, which are suitable for the optimization of the pain points (Low Available Storage Space) as well as variants of the current solution.
Manual High-Bay Racking
- Storage at a height of up to 15 meters
- Operation of the warehouse by forklift trucks
- High flexibility with variable article structure
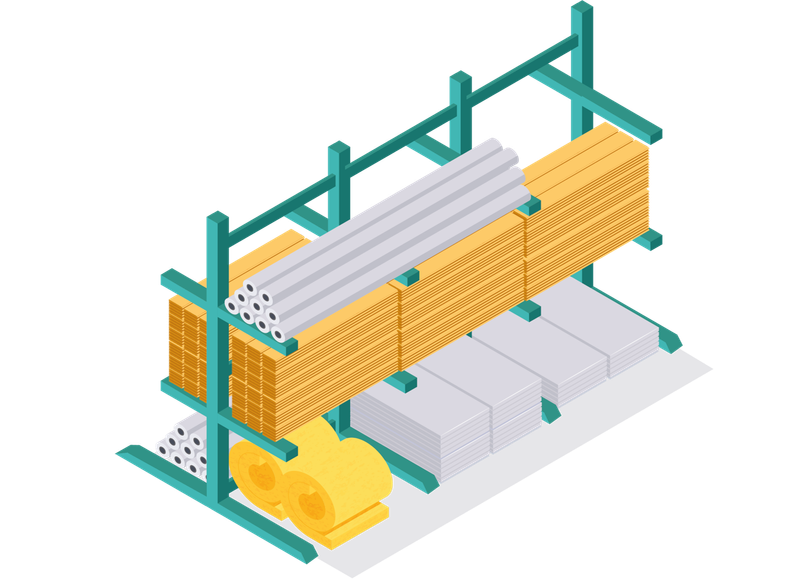
Cantilever Racking
- Storage system for the efficient storage of long, bulky and heavy goods
- High flexibility thanks to modular design
- Suitable for indoor and outdoor use
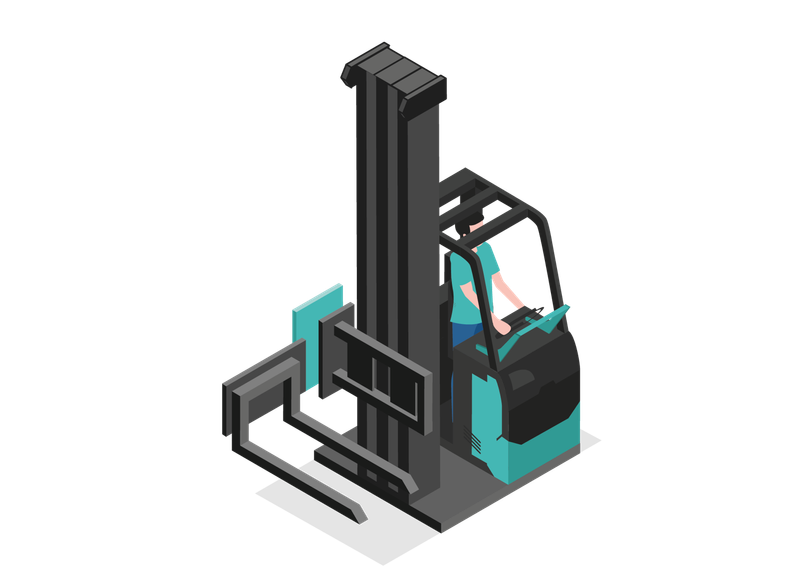
Very Narrow Aisle Truck
- Low aisle width required, enabling high storage density
- Variants available for storage and retrieval, and picking
- Access to high-level storage locations possible

High Lift Order Picker
- Ideally suited for multi-storey warehouse structures
- Man-to-goods picking using a lifting platform for order pickers
- Manual picking without prior relocation
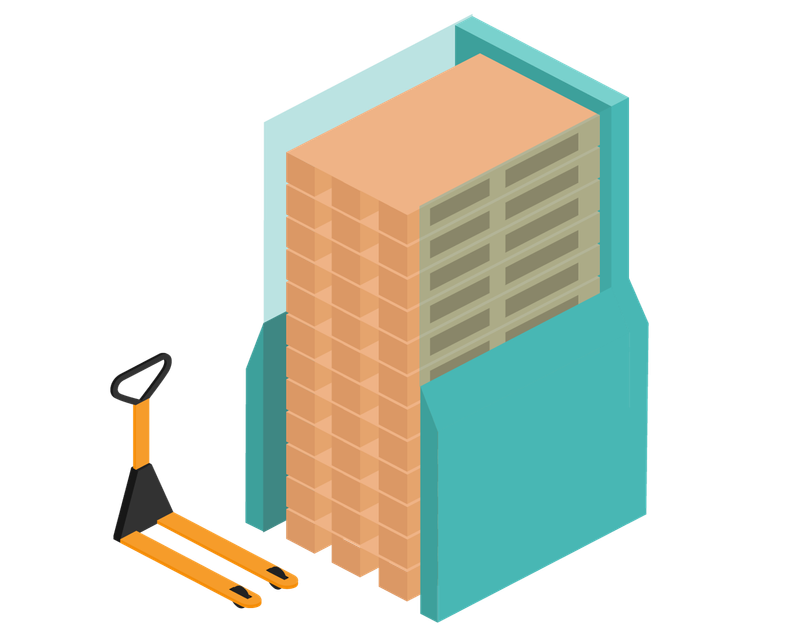
Pallet magazine
- Automated pallet handling
- Improved occupational safety and ergonomics
- Space saving and order in the warehouse
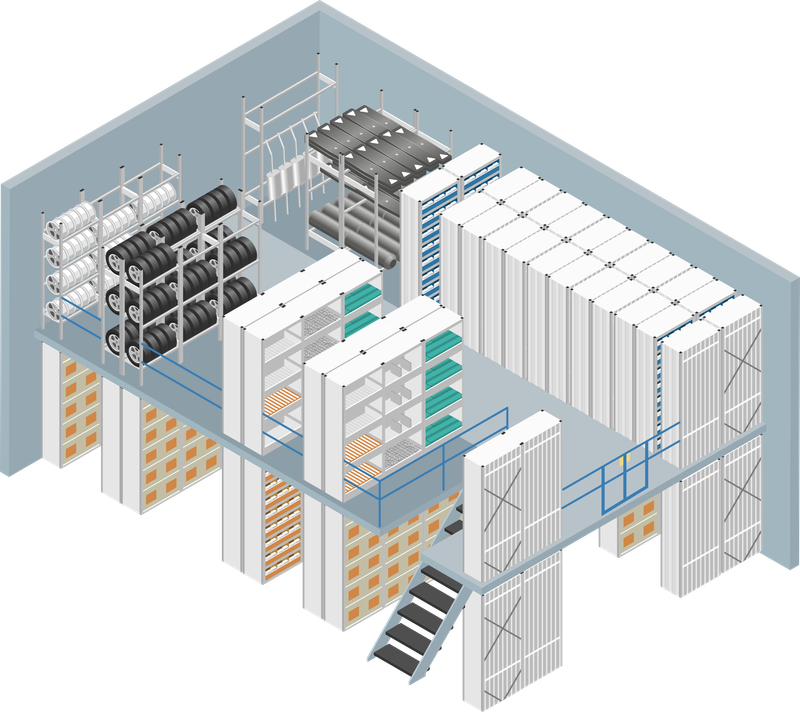
Mezzanine warehouse
- Efficient use of space in warehouses with high ceilings
- Cost savings when expanding storage capacity
- Versatile use possible

-800x700.png)