1
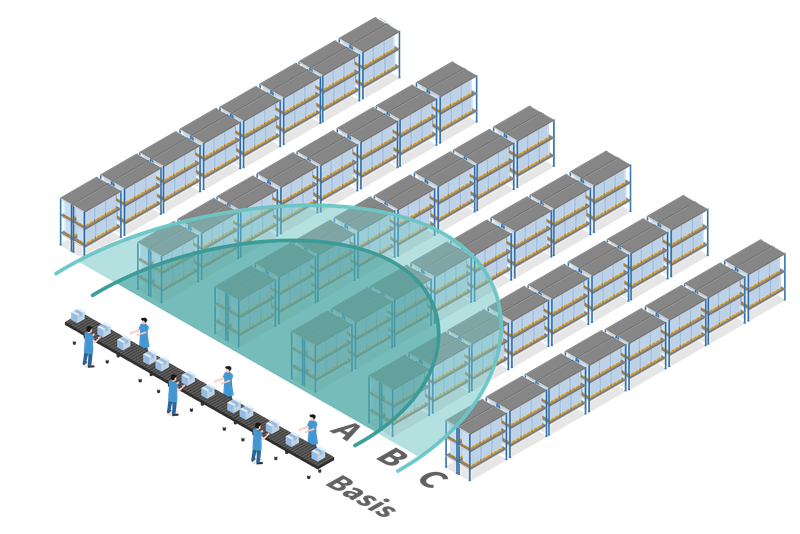
Determination of the Percentage of Locomotion (Walking and Driving)
The proportion of time spent walking and driving can be determined in a number of ways.
A
Motion-Mining®
Within the framework of a Motion-Mining® project, the time share of the activity for a process can be determined.
B
Process Observation and Timing
In a process observation, the proportion of time can be recorded with the help of a stopwatch or a corresponding app.
C
MTM Process Modeling
When planning a process, modelling with MTM can help to determine in advance the expected time share for the activity.
2
Determine Proportion of Drive/Walk Based on Aisle Repetitions
Aisle repetitions are usually inefficient because they lead to duplicate trips. For example, employees have to visit the same aisle several times if items are skipped within a picking tour due to the lack of replenishment.
A
Motion-Mining®
Motion-Mining® can be used to check how often an alley has been visited more than once in a tour.
B
Process Observation and Timing
In a process observation, the frequency of aisle repetitions can be recorded by means of a tally sheet.
C
WMS-Analysis
The WMS data usually shows when and in which aisle picking took place. Analysis can check how often an aisle occurs more than once in a tour if there is at least one entry from another aisle in between.
3
Determination of the Additional Effort
Effort can be determined either by distance traveled or by comparing cycle times.
A
Measure the Layout
An approximation of the distance can be achieved by determining the average paths in the layout. In the next step, the average path length must then be multiplied by the speed of the vehicle/person (see MTM lists).
B
Comparison of Lead Times
Instead of looking at distances, it is possible to look at how the lead time of tours with aisle repetition relates to the lead time of tours without aisle repetition. To do this, in addition to the frequency, the lead time must be determined in the previous step. The potential lies in the reduction of all lead times to the lead time of tours without aisle repetition.
4
Determine the Total Effort
The total cost can be calculated by multiplying the average savings per employee per day by the number of employees per day and the number of working days per year. The total cost is therefore calculated from the hours per year and the cost of one working hour.